No products in the cart.
How to Use Home & Solar Batteries Safely (Real Risks Most People Ignore) Leave a comment
Batteries have become a silent backbone of modern homes. From powering solar systems and UPS backups to running electric bikes and home inverters, we rely on them daily, often without thinking much about safety. I learned this the hard way when a poorly ventilated battery setup in a small solar room began overheating during peak summer. Nothing caught fire, but the smell, heat, and sudden shutdown were enough to show me how critical battery safety really is.
Whether you use lithium batteries, lead-acid batteries, or a hybrid setup for solar power, battery safety is not optional. It directly affects performance, lifespan and most importantly your home and family’s safety.
This guide explains practical, real-world battery safety tips for home and solar use, based on industry best practices, manufacturer guidelines and common mistakes seen in real installations.
Why Battery Safety Matters in Real Homes
In local installations across Pakistan, battery-related issues are one of the most common causes of system failure, not because of defective products but due to poor handling, incorrect charging or lack of ventilation. From overheated UPS batteries in small shops to improperly installed solar batteries in homes, many safety risks are preventable with the right knowledge. This guide is based on practical usage scenarios commonly seen in home and solar setups.
Why Battery Safety Matters More Than Ever
As solar adoption grows, many homes now store large amounts of energy in compact battery banks. Unlike traditional electrical wiring, batteries store chemical energy, which can become dangerous if mishandled.
Poor battery safety can lead to:
- Overheating and thermal runaway
- Fire or explosion risks
- Shortened battery lifespan
- Damage to inverters and appliances
- Costly replacements and system downtime
Organizations like the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) and battery manufacturers such as BYD, CATL and Panasonic consistently emphasize that most battery-related incidents happen due to installation errors, poor ventilation or incorrect charging not battery defects.
Understanding Battery Types Used at Home

Before discussing safety tips, it’s important to understand the common battery types used in homes and solar systems. If you’re unsure which battery technology suits your setup, we’ve explained the differences in detail in our guide on lithium vs lead-acid batteries for solar systems.
Lead-Acid Batteries
- Flooded, AGM, or Gel types
- Lower upfront cost
- Require ventilation and maintenance
- More sensitive to deep discharge
Lithium-Ion / LiFePO₄ Batteries
- Higher energy density
- Built-in Battery Management System (BMS)
- Longer lifespan
- Higher upfront cost but safer when installed correctly
Each battery type has different safety requirements and treating them the same is one of the most common mistakes homeowners make.
1. Install Batteries in a Properly Ventilated Area
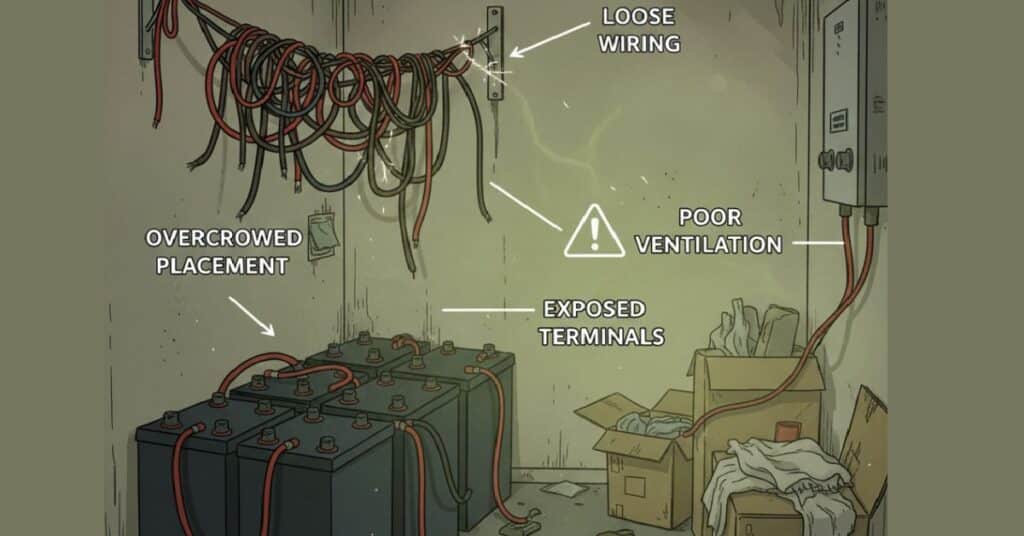
One of the most overlooked safety rules is ventilation.
Why ventilation matters
- Batteries generate heat during charging and discharging
- Lead-acid batteries release hydrogen gas
- Poor airflow increases fire risk and shortens battery life
Best practices
- Batteries should be Installed in a cool, dry and shaded area
- Never place batteries in living rooms or bedrooms
- Avoid sealed cabinets unless designed for batteries
- Leave space between batteries for airflow
A homeowner installed lead-acid batteries in a small storeroom without vents. Over time, hydrogen gas buildup caused corrosion on terminals and inverter failure. Simple ventilation could have prevented it
General battery safety practices, including proper ventilation and temperature control are also emphasized by international consumer safety organizations.
2. Always Use the Correct Charger and Charge Controller
Using the wrong charger is a silent battery killer.
Why this is dangerous
- Overcharging causes overheating
- Undercharging leads to sulfation (lead-acid)
- Incorrect voltage damages lithium cells
Safety checklist
- Match charger voltage exactly (12V, 24V, 48V)
- Use MPPT or PWM charge controllers recommended by manufacturers
- Ensure lithium batteries are paired with lithium-compatible controllers
- Never make a mistake of mixing old and new batteries in the same bank
According to Battery University, incorrect charging profiles are responsible for a significant percentage of early battery failures.
3. Avoid Overloading Your Battery System
Many users underestimate how much load their batteries handle daily.
Many homeowners make this mistake because they don’t calculate power needs properly our article on how to size a home solar battery system walks through this step by step.
Common overload sources
- Adding appliances without recalculating load
- Running air conditioners on undersized battery banks
- Connecting high-surge devices like motors and pumps
Safe approach
- Calculate total wattage before installation
- Maintain a safety margin of at least 20%
- Monitor discharge levels regularly
- Use energy-efficient appliances
Case study:
A small shop added a second freezer to a solar system designed for lighting and fans. Within months, batteries degraded rapidly due to constant deep discharge.
4. Never Ignore Battery Temperature Limits
Temperature is one of the biggest factors affecting battery safety and lifespan.
Recommended ranges
- Lead-acid: 15°C to 30°C
- Lithium (LiFePO₄): 0°C to 45°C (charging range may be narrower)
What happens outside this range
- High heat accelerates chemical degradation
- Cold temperatures reduce capacity and charging efficiency
- Too much heat can cause thermal runaway in lithium batteries
Practical tip
Install a simple digital thermometer in your battery area. It’s a low-cost way to prevent high-temperature damage.
5. Use Proper Fuses, Breakers and Cable Sizes
Electrical protection is non-negotiable for battery systems.
Essential safety components
- DC-rated fuses between battery and inverter
- Circuit breakers for easy isolation
- Correct cable thickness to handle current load
Undersized cables can overheat and melt insulation, causing short circuits.
According to NEC (National Electrical Code) guidelines, DC systems require stricter protection due to sustained current flow.
6. Never Mix Different Battery Types or Capacities
Mixing batteries may seem cost-effective, but it’s unsafe.
Avoid mixing:
- Lithium and lead-acid batteries
- Different brands in one bank
- Old and new batteries together
- Different capacities or chemistries
This causes uneven charging and discharging, increasing failure and fire risk.
7. Handle Batteries with Care During Installation
Physical damage is another major safety risk.
Installation safety tips
- Never drop or tilt lithium batteries excessively
- Avoid metal tools touching terminals
- Wear insulated gloves
- Secure batteries to prevent movement during vibrations
Real example:
A cracked lithium battery casing during transport led to internal cell damage and early failure even though it worked initially.
8. Regularly Inspect and Maintain Your Battery System
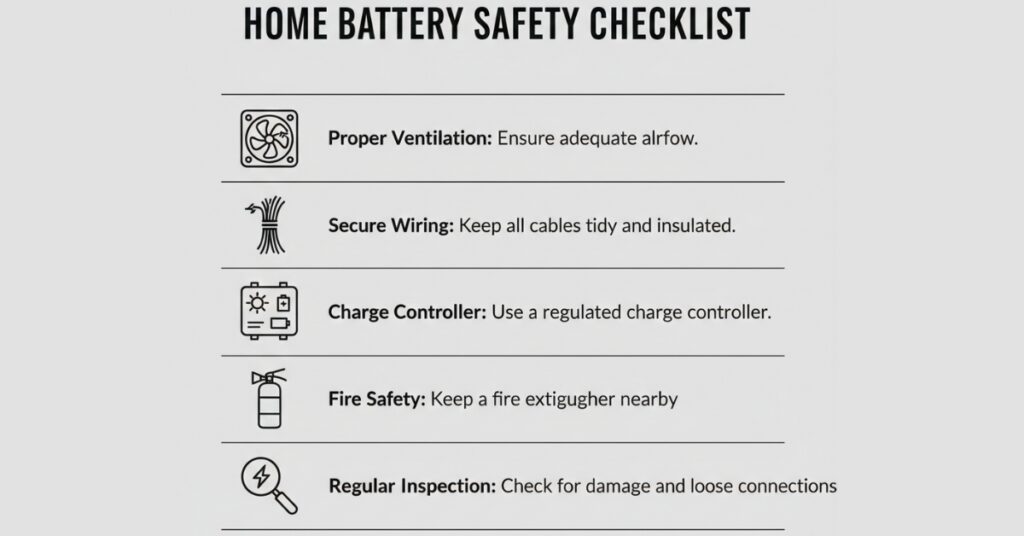
Battery safety isn’t “install and forget.”
Monthly checks
- Look for swelling or leakage
- Check terminal tightness
- Clean corrosion on lead-acid terminals
- Monitor voltage readings
Annual checks
- Professional inspection
- Capacity testing (especially for lead-acid)
- Firmware updates for smart lithium batteries
9. Keep Batteries Away from Water and Moisture
Water and electricity are a dangerous mix.
Safety steps
- Install batteries above ground level
- Avoid damp basements
- Use waterproof enclosures where needed
- Protect outdoor batteries with rated cabinets
10. Follow Manufacturer Guidelines—Always
Every battery manufacturer provides:
- Installation manuals
- Operating limits
- Charging specifications
- Safety warnings
Ignoring these guidelines is one of the fastest ways to void warranties and create hazards.
Reputable manufacturers like Pylontech, BYD, EVE and REPT design batteries to be safe—but only when used as intended.
Battery Safety for Solar Systems in Pakistan
In regions with:
- High temperatures
- Load shedding
- Voltage fluctuations
Battery safety becomes even more critical.
This is especially relevant in high-temperature regions, as discussed in our guide on solar battery performance in hot climates.
Practical Pakistan-specific advice
- Avoid direct sunlight exposure
- Ensure stable grounding
- Use surge protection
- Choose batteries rated for high ambient temperatures
Final Thoughts: Safety Protects Your Investment
Batteries are not just power storage devices—they are long-term investments. A safe battery setup:
- Lasts longer
- Performs better
- Protects your home and family
- Saves money over time
Whether you use batteries for solar backup, UPS systems or electric mobility, following proper safety practices makes all the difference.
Join the Conversation
Have you faced any battery-related issues at home or with your solar system?
Share your experience in the comments.
Your safety and your power matters.


